"People's House: Decoding the Significance of the Indian Parliament"
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
Introduction:
The Indian Parliament stands as a symbol of the world's largest democracy, a vibrant and diverse nation where the voices of over a billion people find representation. Comprising two houses – the Lok Sabha (House of the People) and the Rajya Sabha (Council of States) – the Indian Parliament is a dynamic institution that plays a pivotal role in shaping the country's destiny.
Historical Context:
The roots of the Indian Parliament can be traced back to the colonial era, with the formation of the Imperial Legislative Council in 1861. However, it wasn't until 1950, with the adoption of the Constitution, that the current bicameral structure took shape. Today, the Parliament operates under a federal system, reflecting the rich tapestry of India's linguistic, cultural, and regional diversity.
Functioning of the Lok Sabha:
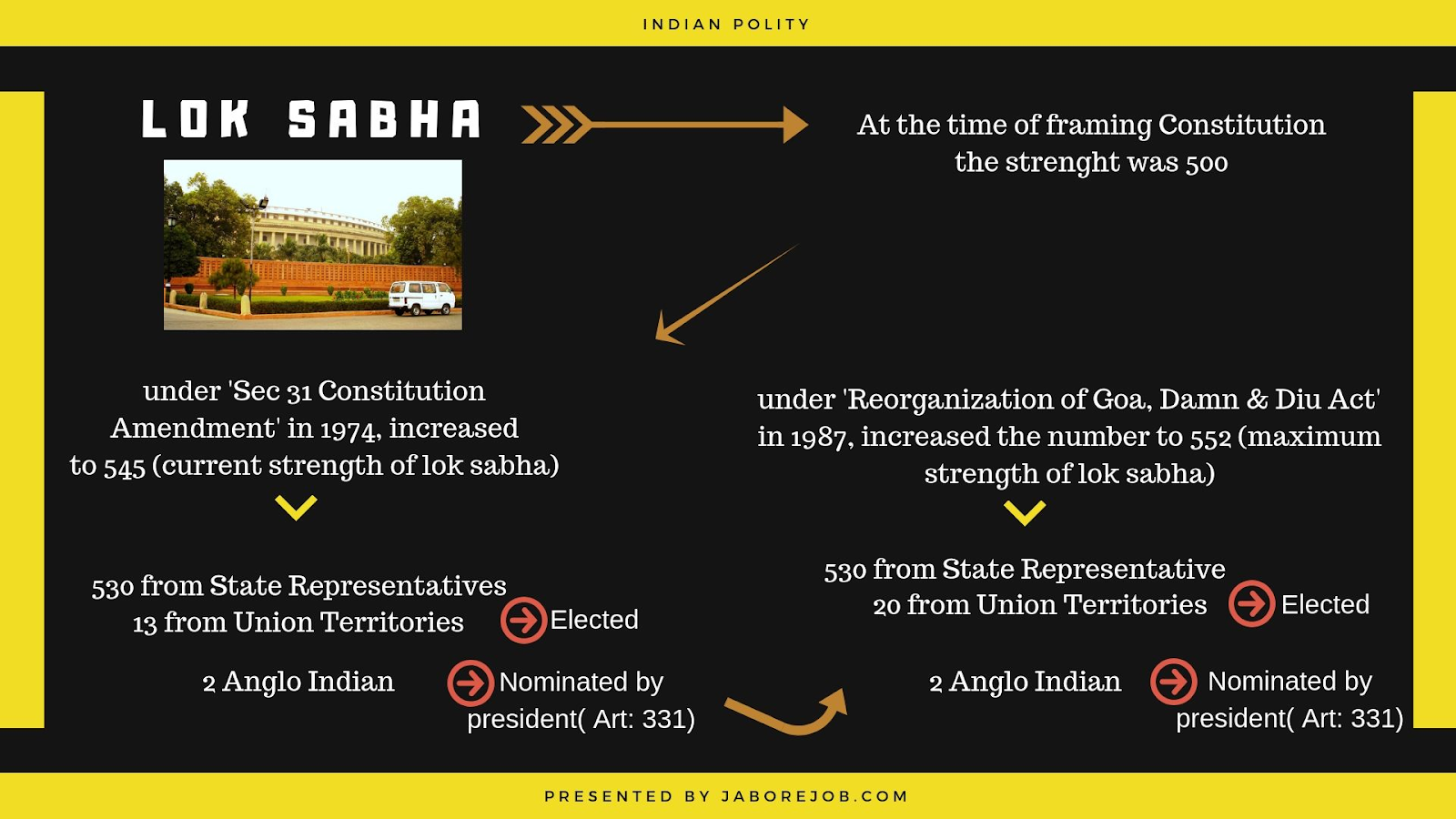
The Lok Sabha, the lower house of Parliament, is the primary legislative body where Members of Parliament (MPs) are directly elected by the people. With 545 seats (including two nominated members), it plays a crucial role in lawmaking, budgetary matters, and holding the executive accountable. The Speaker, elected by the members, presides over the Lok Sabha, ensuring orderly conduct and fair debates.
The Rajya Sabha, the upper house, represents the states and union territories. It consists of 245 members, with 233 elected by the state legislative assemblies and the union territories, and 12 nominated by the President of India for their expertise in various fields. The Vice President serves as the ex-officio Chairman of the Rajya Sabha. Unlike the Lok Sabha, the Rajya Sabha's role extends beyond representing the people, as it acts as a revising chamber, providing a forum for in-depth discussions on legislation.
Challenges and Criticisms:
Despite its critical role in Indian democracy, the Parliament faces various challenges. One significant concern is the frequent disruptions and adjournments during sessions, often hindering the legislative process. Opposition protests, sometimes necessary for highlighting crucial issues, can escalate into chaos, impeding the functioning of the Parliament.
Additionally, the complexity of India's diverse society often leads to demands for more inclusive representation. While strides have been made, there is an ongoing debate about enhancing women's participation and addressing the underrepresentation of certain communities.
The Need for Reforms:
To address these challenges, there is a growing call for parliamentary reforms. Proposals include fixed terms for sessions, stricter regulations on disruptions, and increased transparency in legislative processes. Electoral reforms are also on the agenda, with discussions about the feasibility of simultaneous elections at the national and state levels.
Celebrating Achievements:
Despite the hurdles, the Indian Parliament has achieved significant milestones. Landmark legislations like the Goods and Services Tax (GST) and the Right to Information Act showcase the Parliament's ability to evolve and respond to the changing needs of the nation. The passage of bills addressing social issues, economic reforms, and environmental concerns reflects the diverse and inclusive nature of Indian policymaking.
The Role of Technology:
In recent years, technology has played a crucial role in making parliamentary proceedings more accessible to the public. Live streaming of sessions, online archives, and interactive websites have increased transparency and allowed citizens to engage more directly with the legislative process. Social media platforms have become a powerful tool for MPs to communicate with their constituents and gather public opinions.
Conclusion:
The Indian Parliament stands as a testament to the strength of Indian democracy, navigating challenges while celebrating diversity and inclusivity. As the nation evolves, so must its parliamentary institutions. Reforms, both structural and procedural, are essential to ensure a more efficient, accountable, and representative system. As we reflect on the achievements and challenges, it is clear that the Indian Parliament remains at the heart of the nation's democratic journey, embodying the spirit of unity in diversity.
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps








Comments
Post a Comment