"Simplify Government: A Simple Guide to Types of Government"
Introduction:
Government, in simple terms, is the system that manages and regulates a community or a country. Different societies adopt various types of government to organize and control their affairs. Let's explore some common types of government in an easy-to-understand manner.
Democracy:
- Definition: Democracy is a form of government where the power lies with the people. Citizens have the right to participate in decision-making through voting.
- Example: The United States, India, and many European countries practice representative democracy.
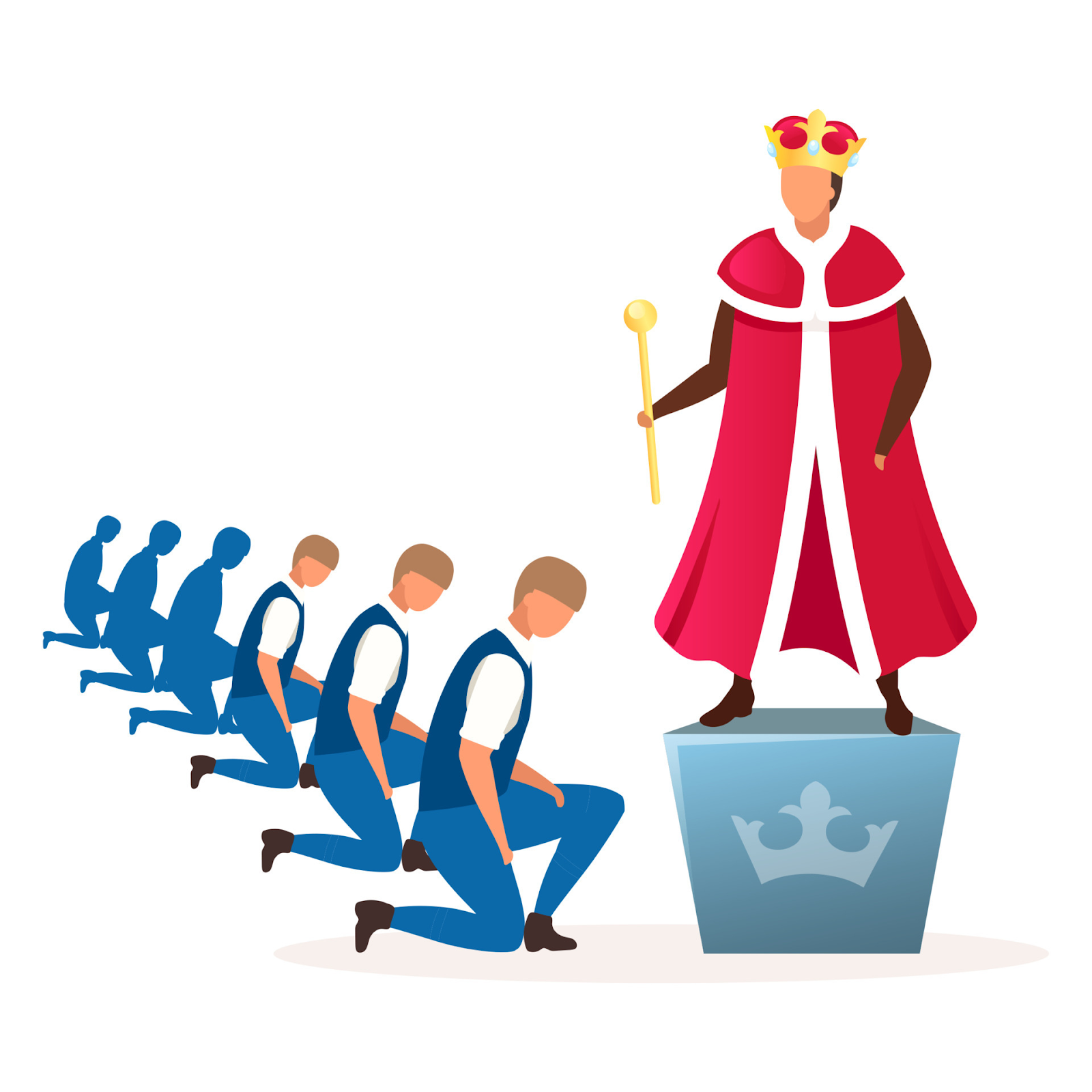
Monarchy:
- Definition: Monarchy is a government led by a single person, often a king or queen, who inherits the position. Power is typically passed down through a royal family.
- Example: The United Kingdom is a constitutional monarchy, where the monarch's powers are limited by a constitution.
Oligarchy:
- Definition: In an oligarchy, a small group of individuals holds significant power and influence over the government.
- Example: Historically, ancient Sparta was considered an oligarchy, where a few wealthy and influential families ruled.
Authoritarianism:
- Definition: Authoritarian governments are characterized by strong central power, limited political freedoms, and strict control over society.
- Example: China is often cited as an example of an authoritarian regime, where the Communist Party holds significant control.
Totalitarianism:
- Definition: Totalitarian governments have absolute control over all aspects of public and private life, including the economy, culture, and individuals.
- Example: North Korea is often described as a totalitarian state, where the government tightly controls all aspects of society.
Republic:
- Definition: A republic is a form of representative democracy where elected officials represent the interests of the citizens.
- Example: The term "republic" is often associated with countries like the United States and France.
Federalism:
- Definition: Federalism divides power between a central government and regional governments, allowing each level to have its own authority.
- Example: The United States operates under a federal system, with powers divided between the national government and individual states.
Communism:
- Definition: In a communist government, there is no private ownership, and the state controls all means of production. The goal is to achieve a classless society.
- Example: The Soviet Union, under leaders like Lenin and Stalin, attempted to establish a communist system.
Socialism:
- Definition: Socialism advocates for collective or governmental ownership and control of the means of production, aiming to reduce economic inequality.
- Example: Sweden is often cited as a country with socialistic policies, combining a market economy with a strong welfare state.
Theocracy:
- Definition: Theocracy is a government where religious leaders or religious institutions hold political power.
- Example: Iran is often cited as an example of a theocratic state, where Islamic clerics play a significant role in governance.
Conclusion:
Understanding the various types of government helps us comprehend the diversity in political systems across the globe. Each form has its strengths and weaknesses, shaping the lives of citizens and influencing the course of history. By appreciating these differences, we can engage in informed discussions about the kind of government that best serves the needs and aspirations of a society.











Comments
Post a Comment